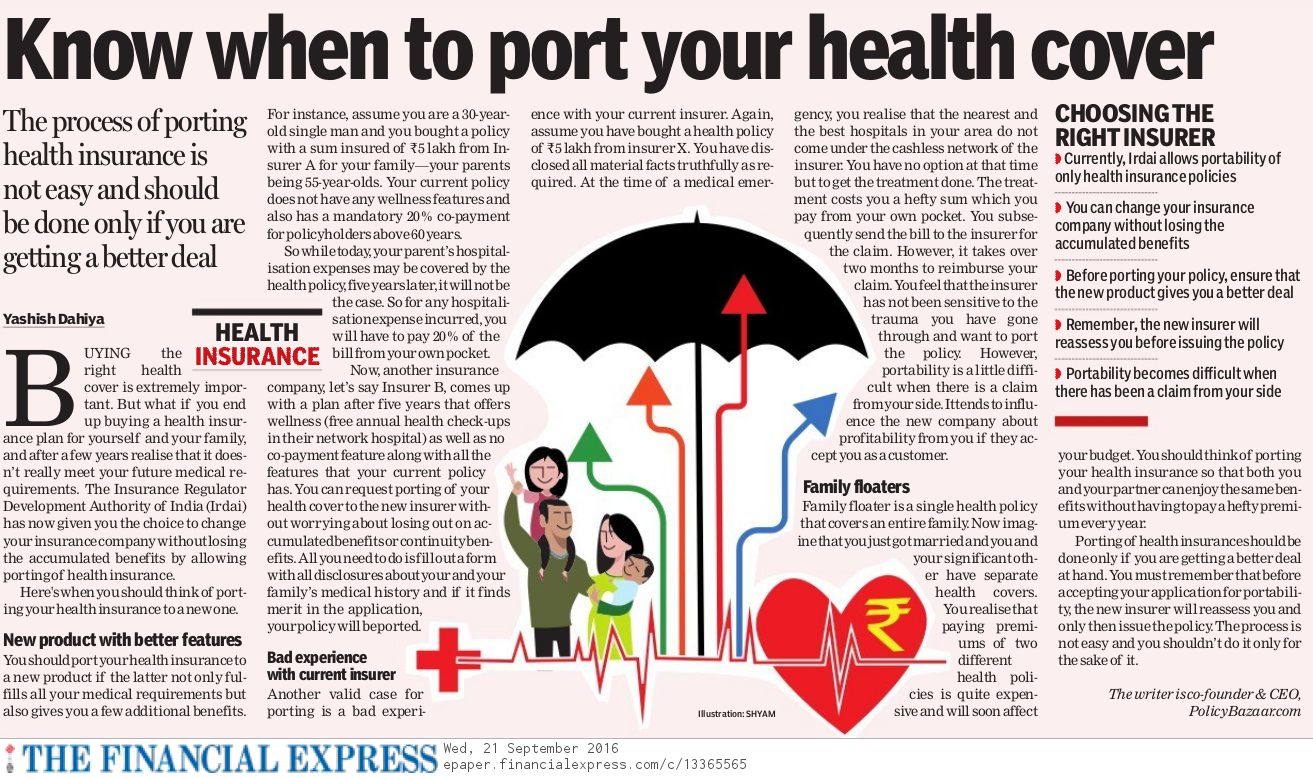
Latest articles on Life Insurance, Non-life Insurance, Mutual Funds, Bonds, Small Saving Schemes and Personal Finance to help you make well-informed money decisions.
You expressly agree the use of the service is at your sole risk. The service is provided on an "as is" and "as available" basis. www.surojitkala.com expressly disclams all warranties of any kind, whether express or implied, including, but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose and non-infringement. www.surojitkala.com makes no warranty the services will meet your requirements, or the services will be uninterrupted, timely, secure, or error free. Nor does www.surojitkala.com make any warranty as to the results that may be obtained through the service or that defects in the software will be corrected. You understand and agree any material and/ or data downloaded or otherwise obtained through the use of the service is done at your own discretion and risk and you will be solely responsible for any damage to your computer systems or loss of data that results from the download of such material and/ or data. www.surojitkala.com makes no warranty regarding any goods or services purchased or obtained through the service or any transactions entered into through the service. No advice or information, whether oral or written, which you obtain from www.surojitkala.com or through the service shall create any warranty not expressly made herein.
You acknowledge that www.surojitkala.com site may contain links to other web sites operated by third parties ("linked sites"). You acknowledge that, when you click on a link to visit a linked site, a frame may appear that contains the www.surojitkala.com logo, advertisements and/ or other content selected by www.surojitkala.com. You acknowledge that www.surojitkala.com and its sponsors neither endorse nor are affiliated with the linked site or any link contained in a link site, or any changes or updates to such sites. You also acknowledge that www.surojitkala.com is providing these links to you only as a convenience.
www.surojitkala.com does not endorse in anyway any advertisers/ contents of advertisers on its webpages. Please therefore verify the veracity of all information on your own before undertaking reliance and actioning thereupon. www.ecrwealth.com shall not be responsible nor liable for any consequential damages arising on account of your relying on the contents of the advertisement.
This site is the responsibility of www.surojitkala.com
We want you to
What Information is, or may be, collected from you?
We will collect certain anonymous information in standard usage logs through our Web server, including: computer-identification information obtained from "cookies," sent to your browser from a
We may collect the following personally identifiable information about you:
Who collects the information?
We will collect anonymous traffic information from you when you visit our site
We will collect personally identifiable information about you only as part of a voluntary registration process.
Our advertisers may collect anonymous traffic information from their own assigned cookies to your browser
The Site contains links to other Web sites. We are not responsible for the privacy practices of such Web sites
We offer a collection of online services which are available to you. Please understand that any information that is disclosed in these areas becomes public information. We have no control over its use and you should exercise caution when disclosing your personal information to anyone.
How's the information used?
We use personal information to:
We use contact information internally to:
Generally, we use anonymous traffic information to:
With whom will your information be shared?
We will not disclose any of your personally identifiable information to third parties unless:
We will not use your financial information for any purpose other than to provide services to you.
What choices are available to you regarding collection, use and distribution of your information?
Supplying personally identifiable information is entirely voluntary. You are not required to register with us in order to use our site. However, we offer some services only to visitors who do register.
Upon request, we will remove your personally identifiable information from our database, thereby canceling your registration.
If we plan to use your personally identifiable information for any commercial purposes, we will notify you at the time we collect that information and allow you to opt-out of having your information used for those purposes.
All sites that are customizable require that you accept cookies. You also must accept cookies to register as someone for access to some of our services. e.g Online Portfolio. For information on how to set your browser to alert you to cookies, or to reject cookies, go to http://www.cookiecentral.com/faq/.
What security procedures are in place to protect information from loss, misuse or alteration?
To protect against the loss, misuse and alteration of the information under our control, we have in place appropriate physical, electronic and managerial procedures. For example, our servers are accessible only to authorized personnel.
Although we will endeavor to safeguard the confidentiality of your personally identifiable information, transmissions made by means of the Internet cannot be made absolutely secure. By using this site, you agree that we will have no liability for disclosure of your information due to errors in transmission or unauthorized acts of third parties.
Policy Updates
We reserve the right to change or update these policies at any time upon reasonable notice, effective immediately upon posting to this site.

 Industry News
Industry News